Honda patents show new front-facing camera for Africa Twin
New patent drawings from Honda reveal a new camera placed at the front of an Africa Twin which would be used to provide data for active riding assists.

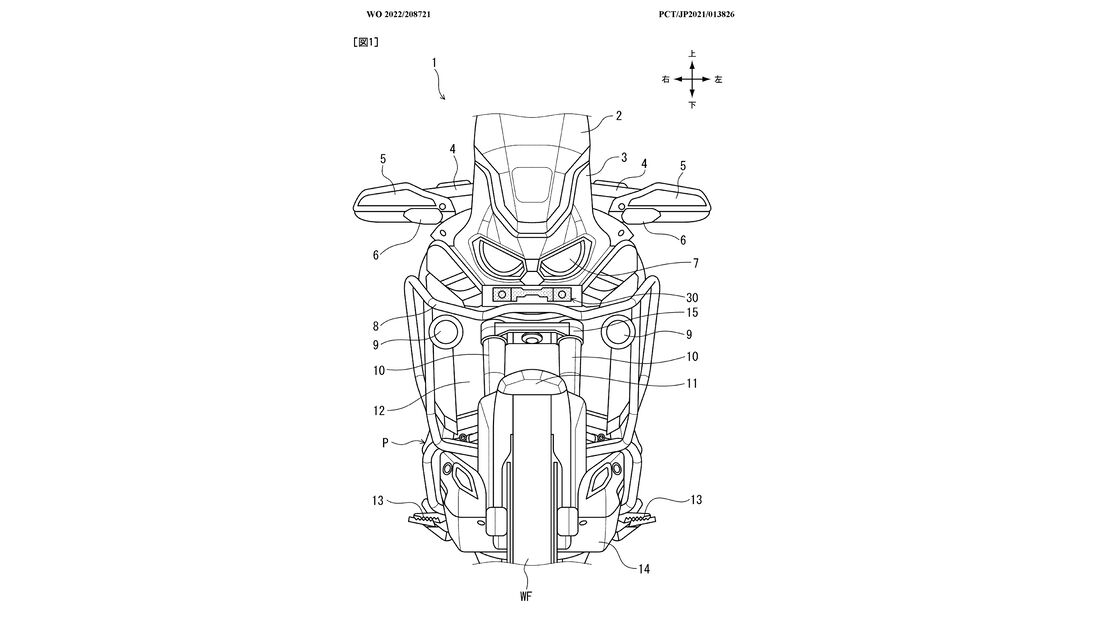
Honda has filed patent drawings which show a new camera on the front of an Africa Twin which would be used for traffic monitoring and providing data to active rider aids.
The camera would operate as one found in a smartphone, so using sensors rather than a lens with variable focus and zoom.
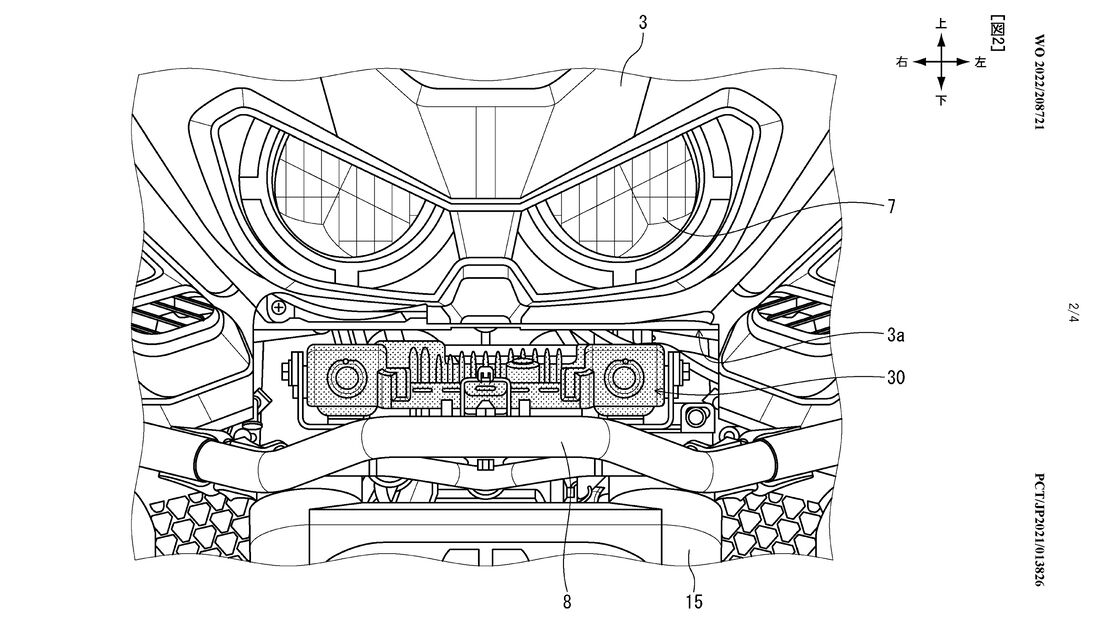
Additionally, Honda has patented its own mount for the camera which, on the Africa Twin would be placed underneath the LED headlights.
Motorrad notes that with the mount in this position the camera is protected from road debris such as stones that could be flicked up from vehicles ahead, as well as from additional light sources that could hinder the camera’s function were it exposed to them.
Further, the patents show that the camera is not fixed in position in the mount, but instead is suspended, and so is protected from vibrations. On an Africa Twin, this has increased importance even compared to Honda’s more solely road-focused models, as its adventurous design means that straying from asphalt to gravel is a commonality. The same could be said about the aforementioned protection from stones.
Although in these patent drawings the camera and mount is specific to the Africa Twin, it would not be unreasonable to expect it to be adapted to Honda’s other models.
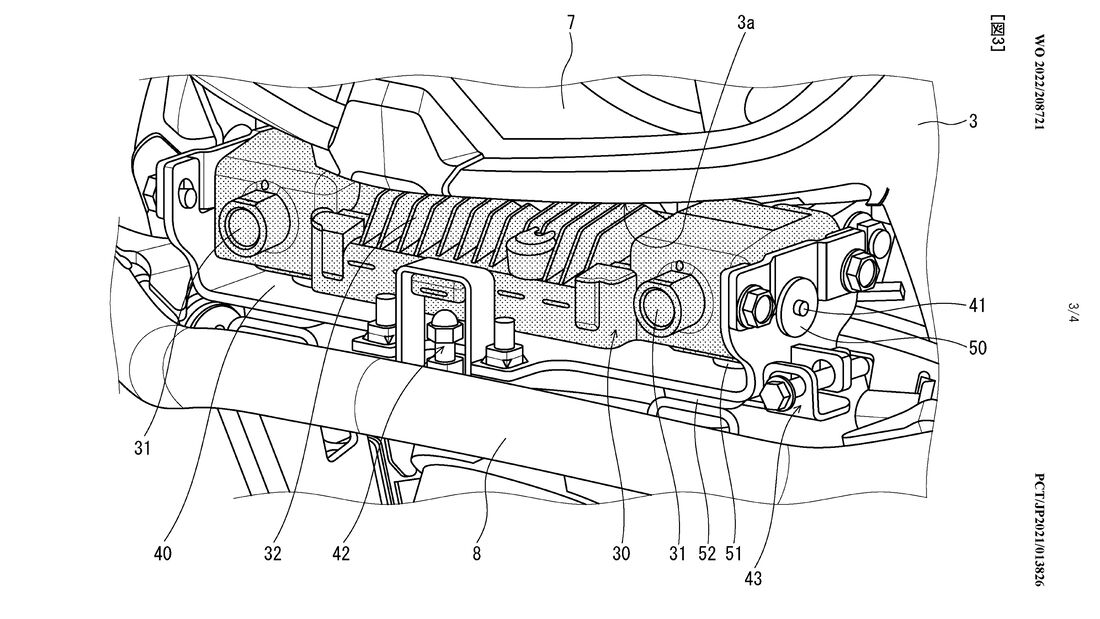
As in the world of cars, motorcycle manufacturers have to consider which type of detection system to use. Honda here has gone with the camera - which is also used by Tesla, for example, on its cars. The advantage here is light perception, but the disadvantage is depth perception.
Alternatives are radar and lidar, but both of these have their drawbacks, too. Lidar requires moving parts, and radar has no light perception so it cannot detect the activation of brake lights, for example.
Images courtesy of Motorrad.

